Enabling and disabling Powershell script execution
If you’ve ever tried to run Powershell scripts from Windows Powershell you’ve probably seen this error message.
e:\testNativex86.ps1 : File e:\testNativex86.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system.
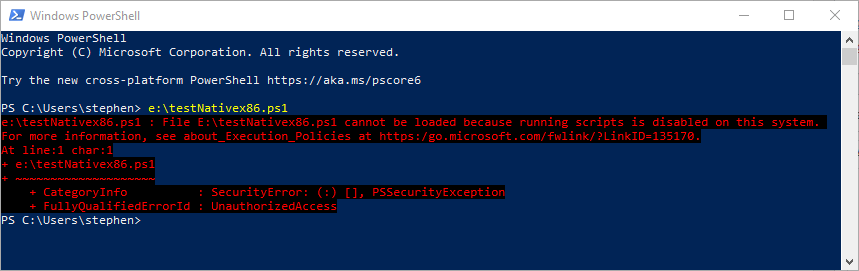
PowerShell restricts script execution by default to protect your system.
Understanding Execution Policies
Execution policies in PowerShell are a key security feature that control how and when configuration files and scripts are loaded and executed. The execution policy affects whether you can run unsigned scripts, scripts downloaded from the internet, or only scripts that are digitally signed. There are several execution policies available, each offering a different level of security and flexibility:
-
Restricted: The default policy, which does not allow any scripts to run. Only individual commands can be executed in the PowerShell window.
-
RemoteSigned: Allows local scripts to run, but requires that scripts and configuration files downloaded from the internet are digitally signed by a trusted publisher. This is a common choice for enabling script execution while maintaining a level of security.
-
Unrestricted: Loads all configuration files and runs all scripts, but will prompt you before running unsigned scripts that were downloaded from the internet. This policy is more permissive and should be used with caution.
-
Bypass: No restrictions; all configuration files and scripts run without warnings or prompts. This is typically used in special scenarios, such as automated tasks where security is managed by other means.
Choosing the right execution policy is important, as it determines how PowerShell handles unsigned scripts, remote signed scripts, and scripts downloaded from the internet. The policy you select directly affects your ability to run scripts and the security of your system.
Default execution policy
The default execution policy for Powershell scripts is Restricted. This means that Powershell scripts cannot execute.
This may seem like an inconvenient setting, but it is setup like this because it minimises the likelihood that a malicious script, downloaded from the internet, or attached to an email will be executed.
To change the execution policy use the Set-ExecutionPolicy command.
Enabling script execution (recommended)
To enable script execution in Powershell open an administrator mode Powershell then type this:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
When prompted answer with: Y
Future attempts to execute scripts will succeed, in this Powershell prompt and in non-administrator mode Powershell prompts.
This is the setting we recommend for most users.
Enabling script execution (less secure)
To enable script execution in Powershell open an administrator mode Powershell then type this:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
When prompted answer with: Y
Future attempts to execute scripts will succeed, in this Powershell prompt and in non-administrator mode Powershell prompts.
Are you sure you need to use this setting? Can you do your work using the RemoteSigned option? If so, please use that.
Enabling script execution (not secure)
To enable script execution in Powershell open an administrator mode Powershell then type this:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass
When prompted answer with: Y
Future attempts to execute scripts will succeed, in this Powershell prompt and in non-administrator mode Powershell prompts.
Only use this if you’re a software developer or IT security professional creating automated tasks.
Disabling script execution
To disable script execution in Powershell open an administrator mode Powershell then type this:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Default
When prompted answer with: Y
The above command sets the execution policy to Default, effectively disabling script execution.
Future attempts to execute scripts will fail, in this Powershell prompt and in non-administrator mode Powershell prompts.
Local Machine or Many Machines?
Setting the policy at the LocalMachine scope applies it to all users on the computer.
Alternatively, you can use Group Policy or the Group Policy Editor (type gpedit.msc in the search bar) to turn on script execution for multiple users or computers. In the Group Policy Editor, navigate to the ‘Turn on Script Execution’ setting to configure execution policies. Execution policies set via Group Policy will override local settings and provide centralized control over script execution.
32 bit Powershell on 64 bit machines
If you’re using a 64 bit machine you’ll notice that the execution policy that you set on the 64 bit Powershell doesn’t affect the 32 bit Powershell, and vice versa.
To enable or disable script execution for 32 bit Powershell you need to open 32 bit Powershell in administrator mode and set the execution policy there rather than in the 64 bit system default Powershell.
Note: If you set the execution policy using the -Scope Process or -Scope CurrentUser parameter, the change only applies to the current process or current session, and will not affect other sessions or system-wide settings.
When you want to run a PowerShell script from the current directory in either 32-bit or 64-bit environments, use the .\ notation (for example, .\yourscript.ps1). This ensures the script is executed from the current directory context, regardless of which version of PowerShell you are using.
The system Powershells are:
| 64 bit | C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe |
| 32 bit | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe |