The Symbol Lookup tab allows you to specify how and where symbolic information is retrieved for your application or service.
The default settings are shown below, although the Visual Studio version may vary.

Compiler / IDE Choice
Use the first combo box to choose which compiler / IDE you used to build your software.
Performance Validator will use the appropriate methods to read your symbols.
The choices are:
•Visual Studio
•Visual Basic 6
•Delphi or C++ Builder
•MingW
•Rust
•Dev C++
•Metrowerks CodeWarrior
•Salford Fortran 95
•Other
Symbol lookup for Microsoft / Intel compilers
•We can provide a Dbghelp.dll  choose one of Performance Validator's known good DbgHelp.dll's based on the version of Visual Studio you are using
choose one of Performance Validator's known good DbgHelp.dll's based on the version of Visual Studio you are using
Performance Validator fetches symbols for your application using an appropriate symbol handler for the type of debugging information you have.
For Microsoft Visual Studio users each version of Visual Studio provides different debugging formats which are readable by the appropriate DbgHelp.dll supplied by Visual Studio. A given version of DbgHelp.dll is usually able to read earlier formats of Microsoft debugging information but is not able to read a future format. For example Visual Studio 2005 (version 8) can read Visual Studio 6 debug information but cannot read Visual Studio 2008 debug information.
Visual Studio 6.0 doesn't supply a DbgHelp.dll so we have provided one for use with Visual Studio 6.0.
Visual Studio 10 is unusual in that the DbgHelp.dll (6.12) supplied by Visual Studio cannot read the debug information created by Visual Studio. To solve this problem we have supplied DbgHelp.dll (6.11) as an alternative.
Performance Validator will choose the appropriate (most recent) version of Visual Studio automatically. You can override Performance Validator's choice by choosing the Visual Studio version from the Visual Studio combo box.
Specify your own DbgHelp.dll
•Or, you may locate a version of DbgHelp.dll  specify your own DbgHelp.dll to use with Performance Validator
specify your own DbgHelp.dll to use with Performance Validator
If you wish to explicitly specify which DbgHelp.dll to use choose the Or, you may locate a version of DbgHelp.dll option enter the path in the DbgHelp.dll edit field or use the Browse... button to select the dbgHelp.dll.
Note that the directory that contains DbgHelp.dll should also contain symsrv.dll if you wish to use symbol servers with Performance Validator.
Don't update DbgHelp.dll
•You're providing your own DbgHelp.dll  use the DbgHelp.dll that ships with your application
use the DbgHelp.dll that ships with your application
If your application needs to use a specific version of DbgHelp.dll that you're already providing with your application you should choose the You're providing your own DbgHelp.dll option to prevent Performance Validator from overwriting your DbgHelp.dll.
Note that the directory that contains DbgHelp.dll should also contain symsrv.dll if you wish to use symbol servers with Performance Validator.
Visual Studio DbgHelp.dll version compatibility
For Microsoft Visual Studio users, each VS version provides different debugging formats which are readable by the appropriate DbgHelp.dll supplied with Visual Studio.
These handlers are usually backwards compatible, but not forwards compatible. For example Visual Studio 2005 (version 8) can read Visual Studio 6 debug information but cannot read Visual Studio 2008 debug information.
Visual Studio 6.0 doesn't supply a DbgHelp.dll so we have provided one for use with Visual Studio 6.0.
Visual Studio 10 is unusual in that the DbgHelp.dll (6.12) supplied by Visual Studio cannot read the debug information created by Visual Studio! To solve this problem we supply version 6.11 as an alternative.
 To see the order in which the DbgHelp.dll process checks directories to find symbols, see the diagnostic tab with the filter set to DbgHelp debug.
To see the order in which the DbgHelp.dll process checks directories to find symbols, see the diagnostic tab with the filter set to DbgHelp debug.
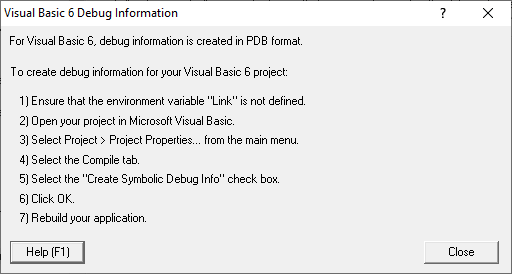
Symbol lookup for other compilers
If you are using another compiler click the link to see information about configuring debug information for that compiler.

After selecting the compiler, clicking the link will show a dialog box containing information relevant to the selected compiler.
For example:
Reset All - Resets all global settings, not just those on the current page.
Reset - Resets the settings on the current page.